iodine orbital diagram|electron dot symbol for iodine : Tagatay The iodine orbital diagram is a graphical representation of the electron configuration of the iodine atom. This diagram shows how the electrons in the iodine atom are arranged in different orbitals. Orbital .
Find out how much baggage you can take on board, as well as info on flying with baggage like sports equipment and Emirates baggage services in Dubai. Skip to the main content Accessibility information. BOOK. Search flights . Cookie Policy; Cybersecurity; Modern Slavery Act transparency statement;
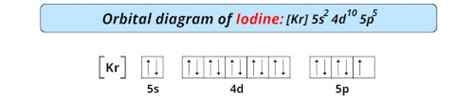
iodine orbital diagram,Atoms can jump from one orbital to another orbital in an excited state. This is called quantum jump. The ground state electron configuration of iodine is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 5s2 5p5. In the iodine ground-state electron configuration, the last electrons of the 5p orbital are located in the . Tingnan ang higit pa
The total number of electrons in iodine is fifty-three. These electrons are arranged according to specific rules in different orbitals. The arrangement of electrons in iodine in . Tingnan ang higit paAtomic energy shells are subdivided into sub-energy levels. These sub-energy levels are also called orbital. The most probable region of electron rotation around the . Tingnan ang higit paScientist Niels Bohr was the first to give an idea of the atom’s orbit. He provided a model of the atom in 1913. The complete idea of the . Tingnan ang higit pa

After arranging the electrons, it is seen that the last shell of the iodine atom has seven electrons. Therefore, the valence electronsof iodine are seven. The elements that have 5, 6, or 7 electrons in the last shell receive the electrons in the last shell . Tingnan ang higit pa
The iodine orbital diagram is a graphical representation of the electron configuration of the iodine atom. This diagram shows how the electrons in the iodine atom are arranged in different orbitals. Orbital . Draw orbital diagram. Before drawing the orbital diagram, you should know the three general rules. Aufbau principle – electrons are first filled in lowest energy orbital and then in higher energy orbital; Pauli .
I (Iodine) is an element with position number 53 in the periodic table. Located in the V period. Melting point: 113.5 ℃. Density: 4.94 g/cm 3 .
Learn about the orbital diagram of iodine, including its electron configuration and the arrangement of electrons in its energy levels. Understand how the orbital diagram . Iodine electron configuration diagram. The electronic configuration of [I] is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4d10 5s2 5p5. The diagram drawn is as follows, where- The s .
Orbital Diagrams. An orbital diagram, like those shown above, is a visual way to reconstruct the electron configuration by showing each of the separate orbitals and the spins on the electrons. This is done by first .Iodine is a chemical element of the periodic table with chemical symbol I and atomic number 53 with an atomic weight of 126.904 u and is classed as nonmetal and is part of .Iodine is purple in color. At room temperature, it is in equilibrium between a solid and gaseous state (see Figure). You can probably draw the Lewis structure and molecular . Atomic spectrum. A representation of the atomic spectrum of iodine. Ionisation Energies and electron affinity. The electron affinity of iodine is 295.2 kJ mol ‑1. The ionisation energies of iodine are given . The second excited state of Iodine Ground state Iodine orbital diagram. The ground state electronic configuration of I is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6 5s 2 4d 10 5p 5 and the orbital diagram is drawn using the following steps. At first, the orbitals are arranged in increasing order of energy. Iodine -. I: properties of free atoms. Iodine atoms have 53 electrons and the shell structure is 2.8.18.18.7. The ground state electron configuration of ground state gaseous neutral iodine is [ Kr ]. 4d10. 5s2. .
In barely words, I need an axis placed left to the diagram with the energy values (e.g. 0.3819 elettronvolt) of the orbitals – user3204810 Commented Oct 30, 2019 at 18:47iodine orbital diagramIodine is a chemical element; it has symbol I and atomic number 53. . 2 is only 256 pm as the missing electron in the latter has been removed from an antibonding orbital, making the bond stronger and hence shorter. In fluorosulfuric acid solution, deep-blue I +
Here is a schematic orbital box diagram for a hydrogen atom in its ground state: . We see that iodine has 5 electrons in the p orbitals. We know that the full p orbitals will add up to 6. Using the Hund's rule and Pauli exclusion principals we .
Energy-Level Diagrams. Because electrons in the σ 1 s orbital interact simultaneously with both nuclei, they have a lower energy than electrons that interact with only one nucleus. This means that the σ 1 s molecular orbital has a lower energy than either of the hydrogen 1s atomic orbitals. Conversely, electrons in the \( \sigma _{1s}^{\star } \) orbital interact .Iodine monochloride is an interhalogen compound with the formula ICl.It is a red-brown chemical compound that melts near room temperature.Because of the difference in the electronegativity of iodine and chlorine, this molecule is highly polar and behaves as a source of I +.Discovered in 1814 by Gay-Lussac, iodine monochloride is the first .
Figure 5.2.1 5.2. 1: Left; A spectroscopic cell containing I2 I 2. Right; A Lewis dot structure and an approximate valence molecular orbital diagram for I2 I 2 (CC-BY-NC-SA; Kathryn Haas) To know what a molecule is at the atomic scale we must use instruments that are more sensitive than our eyes. We know from the Lewis dot structure of I 2 that .iodine orbital diagram electron dot symbol for iodineThe electron configuration for phosphorus is 1s 2 2s 2 2p6 3 s2 3p3 and the orbital diagram is drawn below. 1.4: Electron Configurations and Electronic Orbital Diagrams (Review) is shared under a license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. The electron configuration of an atom indicates the number of valence . Introduction. The electron configuration is the standard notation used to describe the electronic structure of an atom. Under the orbital approximation, we let each electron occupy an orbital, which can be solved by a single wavefunction. In doing so, we obtain three quantum numbers (n,l,m l), which are the same as the ones obtained from .Filling Orbital: 5p 5; Number of Electrons (with no charge): 53; Number of Neutrons (most common/stable nuclide): 74; Number of Protons: 53; Oxidation States: ±1,5,7; . Iodine - I (EnvironmentalChemistry.com)- Comprehensive information for the element Iodine - I is provided by this page including scores of properties, element names in .MO Diagram of I2 MO Diagram of I2-Base Complex. of IodineSUNY College at Oneonta, Bill ViningIodine, 2, is a highly colored, fairly volatile solid. It’s color arises from an Electronic transition from a pi-antibonding orbital to a vacant sig. a antibonding orbital (see figure below left).Although iodine, like all the halogens, is an oxidizing . Physical properties of Iodine. Physical properties of iodine are mentioned below. The pure iodine is solid at STP and it is lustrous metallic gray in color. The melting point of iodine (I 2) is 113.7 °C and its boiling point is 184.3 °C. The atomic mass of iodine is 126.90 u and its density is 4.94 g/cm 3.Question: Which is the correct hybrid orbital diagram representing the hybridization of iodine in ICl5 ? Show transcribed image text. There are 2 steps to solve this one. . Which is the correct hybrid orbital diagram representing the hybridization of iodine in ICl 5 .

Orbital Diagrams for Simple Molecules . In contrast, the LUMO of iodomethane has an appropriate energy, but its shape has a higher density at the iodine end than the carbon end. Thus e.g. . An eigenvalue solution of these equations yields molecule orbitals (also often called canonical or delocalised orbitals), which are rendered visible by .
The allowed values of l depend on the value of n and can range from 0 to n − 1: Equation 2.5.2 l = 0, 1, 2,., n − 1. For example, if n = 1, l can be only 0; if n = 2, l can be 0 or 1; and so forth. For a given atom, all wave functions that have the same values of both n and l .
electron dot symbol for iodineThe 1s orbital at the bottom of the diagram is the orbital with electrons of lowest energy. The energy increases as we move up to the 2s and then 2p, 3s, and 3p orbitals, showing that the increasing n value has more influence on energy than the increasing l value for small atoms. However, this pattern does not hold for larger atoms. I3 MO (Molecular Orbital) Diagram. Triiodide ion is a shining example of 3-center-4-electron chemical bonding. Now, what does it signify? Before that, a brief summary of MO or Molecular Orbital theory is placed before you. . An atom of iodine has the valence orbitals in the below fashion: 5s, 5px, 5py, 5pz.
iodine orbital diagram|electron dot symbol for iodine
PH0 · unabbreviated electron configuration iodine
PH1 · iodine orbital notation
PH2 · i2 molecular orbital diagram
PH3 · ground state electron configuration iodine
PH4 · electron dot symbol for iodine
PH5 · electron dot diagram for iodine
PH6 · electron configuration of iodine
PH7 · bond order for i₂
PH8 · Iba pa